Introduction
A Bayesian network is a directed graph in which each node is annotated with quantitative probability information. The full specification is as follows:
- Each node corresponds to a random variable, which may be discrete or continuous.
- A set of directed links or arrows connects pairs of nodes. If there is an arrow from node
- Each node
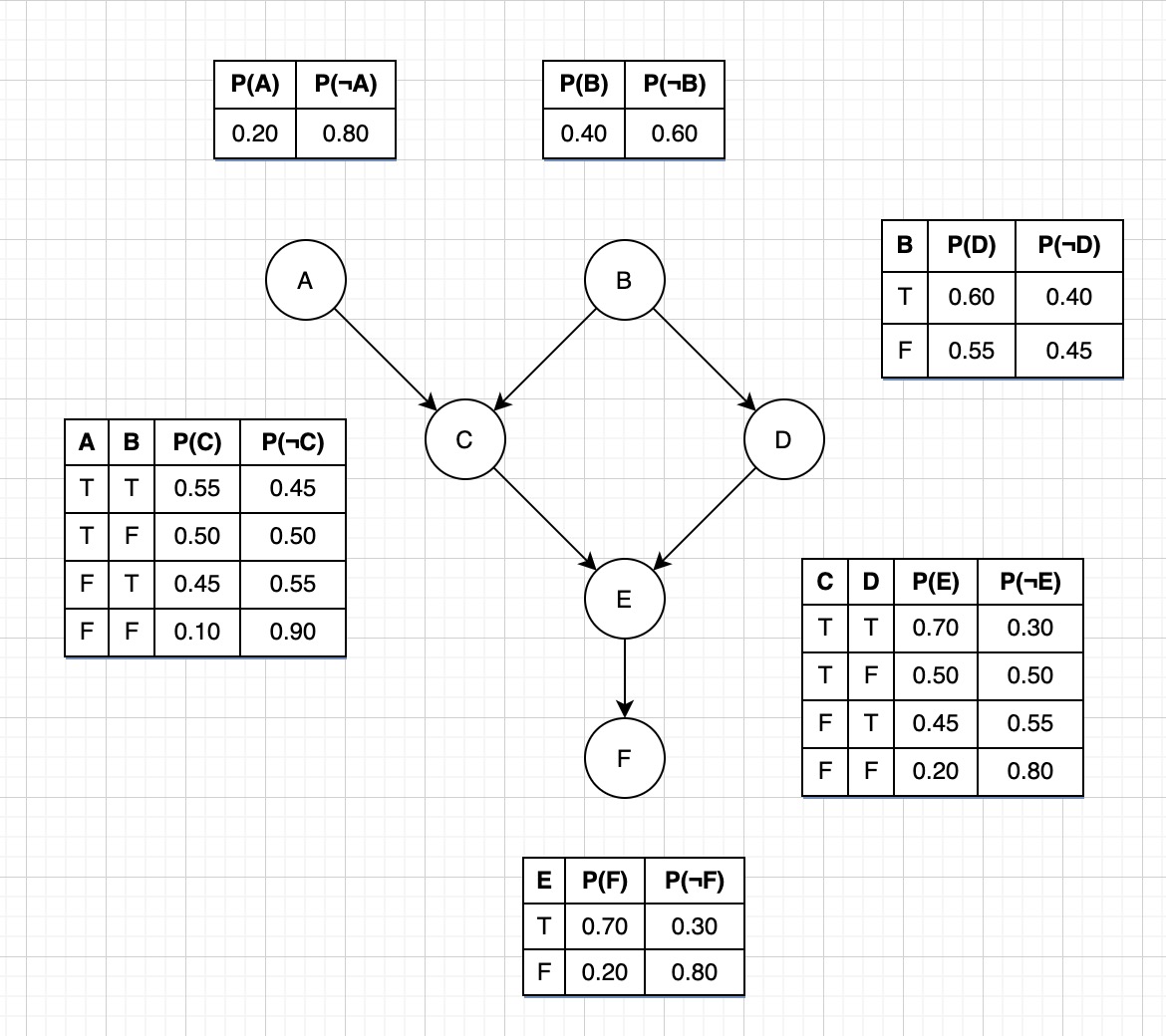
Example Bayesian Network
Semantics of a bayesian network:
- The network is a representation of a joint probability distribution
- Encoding of a collection of conditional independence statements
Full joint distribution
Given by:
Which can be rewritten as:
The above is equivalent to
Provided that
Conditional independence relations in bayesian networks
Steps to determine if two variables are conditionally independent
- Draw the ancestral graph Construct the “ancestral graph” of all variables mentioned in the probability expression. This is a reduced version of the original net, consisting only of the variables mentioned and all of their ancestors (parents, parents’ parents, etc.)
- Moralize the ancestral graph by marrying the parents For each pair of variables with a common child, draw an undirected edge (line) between them. (If a variable has more than two parents, draw lines between every pair of parents.)
- Disorient the graph by replacing the directed edges (arrows) with undirected edges (lines).
- Delete the givens and their edges. If the independence question had any given variables, erase those variables from the graph and erase all of their connections, too.
- Given a query between two variables A, B
- If the variables are disconnected then they’re independent
- If the variables are connected then they’re dependent
- If the variables are missing because they were a given, they’re independent
In the following example we skip step 1 and moralize the entire bayesian network
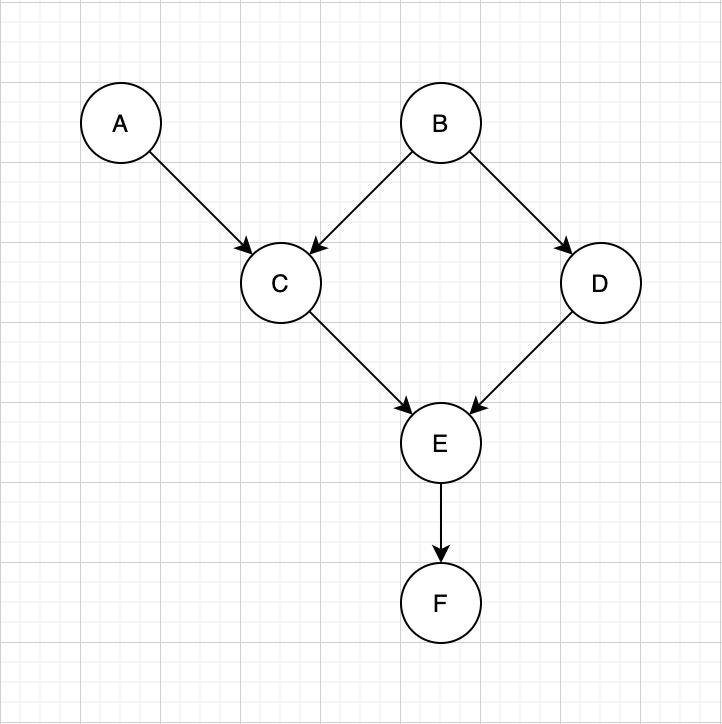
Example Bayesian Network

Example Bayesian Network Moralized
Some conditional independence queries (
- Is
- Is
- Is
- Is
- Is
- Is
- Is
Exact inference
Compute the posterior probability distribution for a set of query values given some observed event (set of evidence variables)
By enumeration
Any conditional probability can be computed by summing terms from the full joint distribution
Working with the example below we can answer some queries:

Example Bayesian Network



