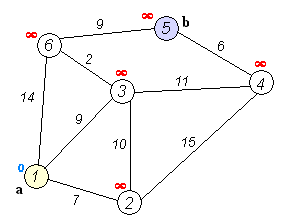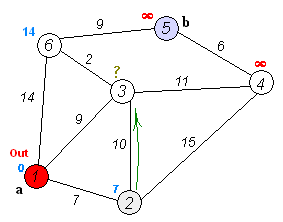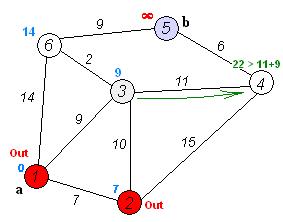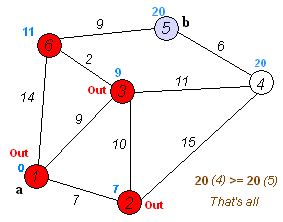
A connected subgraph of
Strongly connected components are useful in a variety of graph algorithms, including finding the shortest path between two vertices, detecting cycles in a graph, and determining the structure of a graph. They can be computed efficiently using algorithms such as Tarjan’s and Kosaraju’s algorithms.
Undirected graphs
The problem of finding components in an undirected graph requires a simple graph traversal starting from an arbitrary vertex, keeping track of the vertices that were already visited. It’s also necessary to run the algorithm above for every vertex of
- The number of components of an undirected graph
vector<bool> visited;
// adjacency list of G
vector<vector<int> > g;
void dfs(int v) {
visited[v] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < g[v].size(); i += 1) {
int next = g[v][i];
if (!visited[next]) {
dfs(next);
}
}
}
/**
* Computes the number of connected components in an undirected graph `G`
* of order `n` and size `m`
*
* Time complexity: O(n + m)
* Space complexity: O(n)
*
* @return {int} The number of components in `G`
*/
int connected_components() {
int n = g.size();
visited.assign(n, false);
int components = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < visited.size(); i += 1) {
if (!visited[i]) {
dfs(i);
++components;
}
}
return components;
}
Directed graphs
Given a directed graph
A strongly connected component (SCC) of
- For any
- For any
Tarjan’s algorithm
The idea is to perform a DFS from an arbitrary vertex (conducting subsequent DFS from non-explored vertices). During the traversal, each vertex
- The time it was explored, denoted as
- The smallest index of any node known to be reachable from
Let
Let
A stack is also needed to keep track of the nodes that were visited. The working of the stack follows the invariant: a node remains on the stack after exploration if and only if it has a path to some node earlier in the stack.

// adjacency list of G
vector<vector<int> > g;
int time_spent;
// the number of scc
int total_scc;
// the time a vertex was discovered
vector<int> time_in;
// the smallest index of any vertex known to be reachable from `i`
vector<int> back;
// the scc vertex `i` belongs to
vector<int> scc;
// invariant: a node remains in the stack after exploration if
// it has a path to some node explored earlier that is in the stack
vector<bool> in_stack;
stack<int> vertices;
void dfs(int v) {
int next;
// the lowest back edge discovery time of `v` is
// set to the discovery time of `v` initally
back[v] = time_in[v] = ++time_spent;
vertices.push(v);
in_stack[v] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < g[v].size(); i += 1) {
next = g[v][i];
if (time_in[next] == -1) {
// unvisited edge
dfs(next);
// propagation of the lowest back edge discovery time
back[v] = min(back[v], back[next]);
} else if (in_stack[next]) {
// (v, next) is a back edge only if it's connected to a predecessor
// of `v`, i.e. if `next` is in same branch in the dfs tree
//
// an alternative is to use the time a vertex finished exploring its
// adjacent nodes, if the time is not set then it's a back edge
back[v] = min(back[v], time_in[next]);
}
}
// if the root node of a connected component has finished
// exploring all its neighbors, assign the same component `id`
// to all the elements in the scc
if (back[v] == time_in[v]) {
total_scc += 1;
do {
next = vertices.top();
vertices.pop();
in_stack[next] = false;
scc[next] = total_scc;
} while (next != v);
}
}
/**
* Finds the strongly connected components in a digraph `G` of order `n`
* and size `m`
*
* Time complexity: O(n + m)
* Space complexity: O(n)
*
* @returns {int} the number of strongly connected components
*/
int tarjan() {
int n = g.size();
scc.assign(n, -1);
time_in.assign(n, -1);
back.assign(n, -1);
in_stack.assign(n, false);
while (!vertices.empty()) {
vertices.pop();
}
time_spent = 0;
total_scc = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 1) {
if (time_in[i] == -1) {
dfs(i);
}
}
return total_scc;
}