Kafka
https://www.slideshare.net/mumrah/kafka-talk-tri-hug
Key Choices
- pub/sub messaging pattern
- messages are persistent (stored in disk)
- consumer keep their own state (stored in zookeeper)
Technology Summary
| Concept | Notes |
|---|---|
| Brokers | Receive messages from producers (sequential write, push) and deliver messages to consumers (sequential read, pull) Messages are flushed to append-only log files |
| Topics | Logical collection of partitions mapped across many brokers |
| Partition | Physical append-only log files, a broker contains some of the partitions for a topic |
| Replication | Partitions are replicated, one broker is the leader and all writes/reads must go through it (replication is for fault tolerance only), replication can be tuned to write to N replicas |
| Producer | Responsible for load balancing messages among brokers, they can discover all brokers from a single one High level api: Producer#send(String topic, K key, V value) Determines the partition based on the key (default hash mod) e.g. send("A", "foo", message) in the example below: "foo" mod 2 No total ordering across partitions Guaranteed ordering inside the partition. Useful if the key is a PK, if so all the messages related with that key will be ordered. |
| Consumer | Request a range of messages from a broker, responsible for their own state i.e. its own iterator High level api: Map<String, List<KafkaStream>> Consumer.connector(Collections.singletonMap("topic", nPartitions)) Blocking/non blocking behavior |
| Consumer Group | Multiple consumers can be part of a consumer group coordinated with zookeeper, in a group each partition will be consumed by exactly one consumer Consequence: broadcast/pubsub (If all the consumer instances have different consumer groups) and load balance/queue (If all the consumer instances have the same consumer group) |
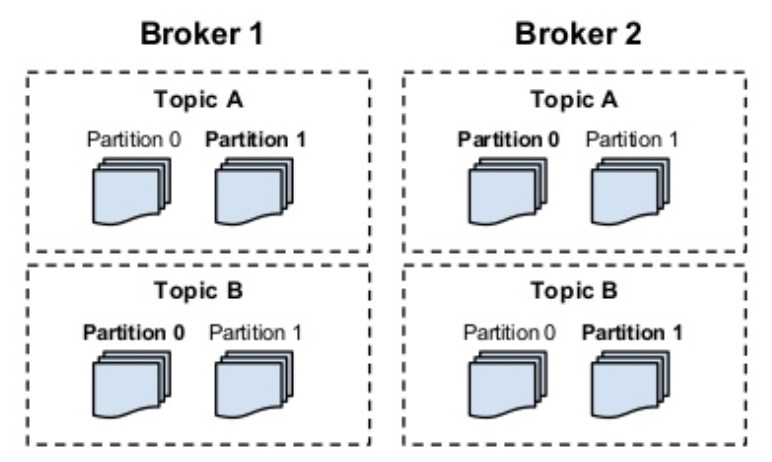
Broker - Partition - Topic
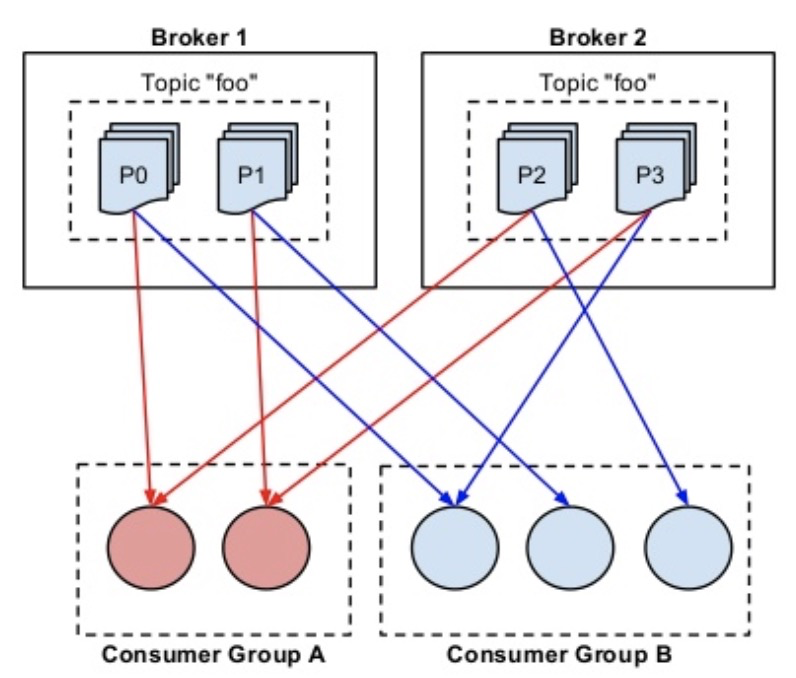
Consumer Groups
Useful numbers
- 50MB/s (producer throughput), 100 MB/s (consumer throughput)
- https://engineering.linkedin.com/kafka/benchmarking-apache-kafka-2-million-writes-second-three-cheap-machines
Applications
- Notification: A updates a record and sends a “record updated” message, B consumes the message and asks A for the updated record to sync its copy
- Stream Processing: Data is produced and written into kafka, consumer groups process these messages and write them back to kafka